Micropiles, also known as minipiles, are a deep foundation element constructed using high-strength, small-diameter steel casing and/or threaded bars or simply constructed as small diameter concrete bored pile with normal steel bars.
Common uses
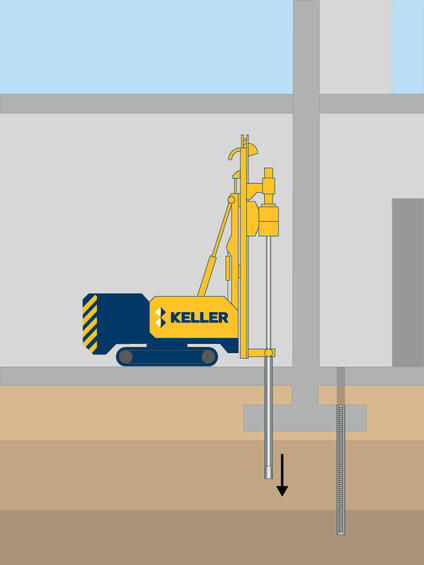
Process
Micro piles can be installed by various means depending on ground conditions and load requirements. Most commonly, micro piles are designed so that their load bearing capacity is essentially derived from the cross section of the high yield steel reinforcement or tube. The grout or concrete cover provides the protective cover but may also be designed to contribute to the external capacity of the micro pile by virtue of skin friction.
Depending on the micro pile diameter the collapsible part of the soil is cased temporarily and the pile is bored using appropriate tools such as an auger or drill bits for granular material and down the hole (DTH) hammers for rock profiles.
Micro piles have been designed for capacities of 1000kN or more in compression or tension.
In highly corrosive environments prefabricated high-yield steel bars are used in micro piles with single, double or triple corrosion protection with minimal grout cover to fill the borehole.
Advantages
Quality assurance
Keller installs micro piles as per American or European standards for design and quality control requirements for execution.