Bored piles are a very effective, state-of-the-art construction element with many applications in foundation and civil engineering. Temporary and permeant steel casings are used for a number of engineering reasons.
Common uses
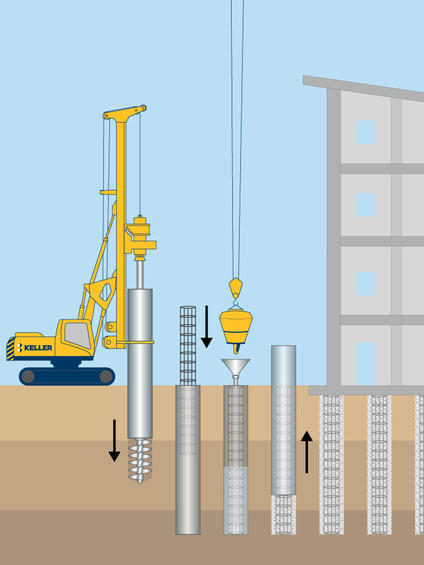
Process
A casing is installed by rotation, oscillation or vibration, soil drilled out using specialised tools, and additional lengths of casing(s) jointed and installed to a predetermined depth. Full length reinforcing steel is then lowered into the hole which is then filled with concrete. Temporary casings are then recovered.
Advantages
Quality assurance
[Company] uses a variety of quality assurance methods for our products including top down and integrity testing, bottom bi-directional pile load tests, and digital recording and logging of the execution parameters.
A range of digital and physical tools including inclinometers, guide walls and GPS equipped total stations can be used to assure plan position and verticality.